Announcements
Home
Upcoming Programmes for Admission
 Centenary Celebrations
Centenary CelebrationsCentenary Celebrations
 Admissions
Admissions Academics
Academics Student Life
Student Life| PI Details | Co-PI Details |
|---|---|
|
Dr. Vasundhara Singh
Designation: Professor |
Dr. Navneet Agnihotri
Designation: Professor |
| Funding Agency | Project Cost |
|---|---|
| Department of Science and Technology-Science and Engineering Research Board (DST-SERB) |
Rs. 27,75,520 |
| Start Date | Completion Date | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 2017-07-05 | 2021-07-04 | Completed |
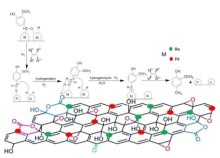
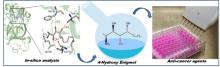
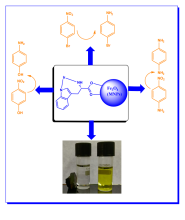
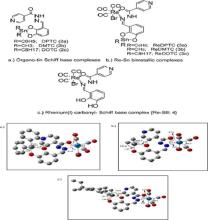
- Enigmol, a known anti-cancer 1-deoxyshingolipid and its stereo isomers have been synthesized by a new route starting from the chiral pool using both isomers of L-alanine via Stereoselective Grignard reaction and Cross metathesis reaction as the key steps.
- The Enigmol analogues have been synthesized by varying chain lengths and an additional additional hydroxyl group on the C-4 position of Enigmol and its chain analogues. The key reaction involved the installation of different lipophilic chain lengths via stereoselective cross metathesis reaction followed by mCPBA epoxidation, Red-Al ring opening and deprotection for the chain analogues and OsO4/NMO mediated dihydroxylation for the 4-hydroxy substituted analogues on the earlier synthesized 1-deoxysphingosines.
- The butyrate ceramides of the 1-deoxysphingosines have been synthesized using the oleic acid and butyric acid, a known chemo-preventative agents via N-Acylation using p-nitrophenyl oleate and butyrate respectively.
- A library of peptidomimetic 1-deoxysphingosine ceramides by Multi Component UGI Reaction have been synthesized using different aldehydes, cyclohexyl isocyanide and butyric acid with the previously synthesized 1- deoxysphingosine
- The in-vitro biological evaluation has been done on the PC-3 and HCT-116 cell lines and the IC50 value have been calculated giving the encouraging results
| Manpower Sanctioned/Hired | Manpower Trained |
|---|---|
|
JRF- One (1) |
Ph.D Produced- One (1) |
| PI Details | Co-PI Details |
|---|---|
|
Dr. Vasundhara Singh
Designation: Professor |
Dr. Satwant Kaur Shahi
Designation: Principal |
| Funding Agency | Project Cost |
|---|---|
| DRDO-TBRL |
Rs. 22.34 Lakhs |
| Start Date | Completion Date | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 2018-09-26 | 2021-10-15 | Completed |
1) A new series of Energetic Ionic Liquid based salts were prepared with good oxygen balance based on urotropine, tetrazolium and triazolium.
2) A library of 3-amino-1,2,4-triazolium based salts by using aminotriazolone, nitrotriazolone, dinitrotriazolone and tetrazolone was synthesize.
3) EIL 3-amino-1,2,4-triazolium perchlorate was found to be highly sensitive towards impact and friction.
4) A new series of EIL/salts were prepared which exhibited good oxygen balance using 5-Aminotetrazolium perchlorate synthesized and showed excellent
5) A library of 1-H-2,3,4,5-tetraazolium based salts in combination with aminotriazolone, nitrotriazolone, dinitrotriazolone and tetrazolone was synthesized.
6) The impact and frictional sensitivity measurements was investigated at DRDO-TBRL and the as synthesized salts were found to be highly explosive in nature.
| Manpower Sanctioned/Hired | Manpower Trained |
|---|---|
|
JRF- One (2) |
Two (2) |
|
Sr. No. |
Sanctioned List |
Procured (Yes/No) Model & make |
Cost (Rs inlakhs) |
Working (Yes/No) |
Utilization Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1. |
IKA RET Magnetic Stirrer |
Yes |
94,890.00 |
Yes |
100 |
|
2. |
Chiller with Vacuum Pump as accessory |
Yes |
2,07795 |
Yes |
100 |
|
3. |
Multifunction Printer Mf246Dn |
Yes |
24,799 |
Yes |
100 |
|
4. |
Melting point |
Yes |
24,072 |
Yes |
100 |
|
5. |
Fridge |
Yes |
12,499 |
Yes |
100 |
|
6. |
Microwave |
Yes |
5,799 |
Yes |
100 |
|
7. |
Constant voltage transformer |
Yes |
15,340 |
Yes |
100 |
| PI Details | Co-PI Details |
|---|---|
|
Dr. Kusum Harjai
Designation: Professor |
Dr. Sanjay Chhibber
Dr. Sanjay Chhibber Dr. Vasundhara Singh |
| Funding Agency | Project Cost |
|---|---|
| Department of Science and Technology- Science Engineering Research Board |
Rs. 36,77,434 |
| Start Date | Completion Date | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 2018-12-15 | 2021-12-15 | Completed |
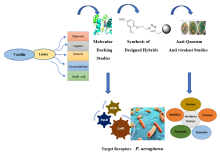
The conjugate was found to be QS inhibitor. It also showed potent in vitro inhibitory activity against biofilm formation due to reduction in twitching, swimming, and swarming motilities of P. aeruginosa. In silico molecular docking studies suggested that PZC 4 binds with the FptA, the outer membrane receptor of pyochelin indicating delivery of conjugate hence zingerone, inside the target organism. PZC possess therapeutic value as a ‘Trojan Horse’ entity and conjugate is transported inside the bacterium effectively through iron transport system after binding with siderophore receptor. PZC has been shown to have hepatoprotective potential in P. aeruginosa induced peritonitis mice model Therefore, this represents an innovative approach against multi-drug resistant Gram-negative bacterium P. aeruginosa. Hence, this study opens a path to employ PZC as potential drug candidate to suppress P. aeruginosa mediated infections. It can help in overcoming resistance.
| Manpower Sanctioned/Hired | Manpower Trained |
|---|---|
|
JRF- 1 |
PhD produced- 1 |
|
Name of Equipment |
Make & Model |
Year of Purchase |
Cost |
Salient features of Equipment |
Condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
UV-Spectrophotometer |
LabIndia |
2019 |
3,67,458 |
Spectrophotometer to observe the optical density |
Working |
|
HPLC Columns |
Sunfire C-18 RP |
2019 |
80,000 |
Columns of HPLC |
Working |
| PI Details | Co-PI Details |
|---|---|
|
Dr Uma Batra
Designation: Professor |
| Funding Agency | Project Cost |
|---|---|
| Ministry of Steel, GOI |
189 Lakh |
| Start Date | Completion Date | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 2019-12-06 | Ongoing |
The project aimed to develop and optimize Austempered Ductile Iron (ADI) technology for use in the agricultural and automotive industries in India. The objectives included studying the mechanical properties of ADI, developing cost-effective production processes, and evaluating its potential applications in Agricultural and Automotive Industry in India.
| Manpower Sanctioned/Hired | Manpower Trained |
|---|---|
|
JRF (Nos): 01 |
Ph.D Produced: 01(In progress) |
|
Name of Equipment |
Make & Model |
Year of Purchase |
Cost (Rs, in Lakh) |
Salient Features of Equipment |
Condition (Working /Not Working) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ADI Pilot Plant |
HiTemp, Bangalore |
2021 |
52.45851 |
200Kg Gross capacity |
working |
|
Servo Hydraulic Fatigue testing Machine of capacity 250 KN |
HEICO, N. Delhi |
2021 |
45,36,240 |
250 KN, 0.01-25Hz |
working |
|
Pin/Ball on disc wear friction monitor |
Magnum, Bangalore |
2021 |
5.6019 |
1-200N, up to 2000RPM |
working |
| PI Details | Co-PI Details |
|---|---|
|
Dr Uma Batra
Designation: Professor |
Dr Kamal
Designation: Assistant Professor |
| Funding Agency | Project Cost |
|---|---|
| SERB, DST, New Delhi |
77,38,525/- |
| Start Date | Completion Date | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 2017-08-28 | 2020-09-27 | Completed |
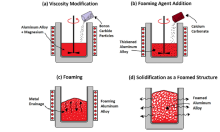
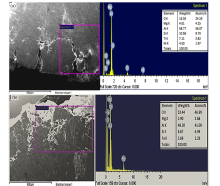
Two types of bone plates have been designed and developed from ZM21 Mg Alloy for the forearm of an adult- non-perforated bone plate and perforated bone plate. The WEDM (for machining contours of bone plate) and EDD processes (for creating interconnected micro-holes in bone plate) used in the development have been optimized for better surface integrity, low degradation rate and apatite formation rate in biological fluid over the expected bone healing period. A comprehensive study on the mechanical integrity loss (i.e, elastic modulus, compressive strength, fatigue strength, bending strength and fracture toughness) of perforated and non-perforated bone plates at regular intervals during complete degradation test period. Correlation between processing parameters (WEDM & EDD) have been established with surface characteristics, degradation rate, apatite formation rate and mechanical integrity of ZM 21 Mg-alloy to predefine the life span of bone plate.
| Manpower Sanctioned/Hired | Manpower Trained |
|---|---|
| JRF (Nos): 01 |
Ph.D Produced: 03 |
|
Name of Equipment |
Make & Model |
Year of Purchase |
Cost |
Salient Features of Equipment |
Condition (Working /Not Working) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CNC Wire EDM setup with accessories |
Ecocut, Electronica India Ltd. |
2018 |
24,95,700/- |
5-axis CNC Wire EDM |
Working |
|
Computerized Universal Testing Machine |
HEICO, |
2018 |
25,20,000/- |
Fatigue Rated Machine 25KN |
Working |
|
Stereo Zoom Microscope |
Carl Zeiss, Stemi Trino 305 |
2018 |
2,28,000/- |
Magnification: 4X |
Working |
| PI Details | Co-PI Details |
|---|---|
|
Dr T K Jindal
Designation: Professor |
| Funding Agency | Project Cost |
|---|---|
| TBRL Chandigarh |
Rs. 9.38 |
| Start Date | Completion Date | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 2016-07-27 | 2019-03-31 | Completed |
The project form TRRL was undertaken the development of PDE combustor with flow control system, fire control system and data acquisition from the no of tests. The development was undertaken successfully and the firing proved to be consistent every time. The data w.r.t pressure and thrust was captured for the tests and the performance curves were obtained.
| Manpower Sanctioned/Hired | Manpower Trained |
|---|---|
|
Ph.D Produced: 2 |
|
Name of Equipment |
Make & Model |
Year of Purchase |
Cost |
Salient Features of Equipment |
Condition (Working /Not Working) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Flow control system |
|
|
5.00 Lakh |
Flow control system for Acetylene and oxygen flow control |
Working |
| PI Details | Co-PI Details |
|---|---|
|
Dr T K Jindal
Designation: Professor |
| Funding Agency | Project Cost |
|---|---|
| Aeronautical Research and Development Board, DRDO, New Delhi |
Rs. 29.10 Lakh |
| Start Date | Completion Date | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 2017-06-16 | 2020-03-31 | Completed |
The project form ARDB was undertaken for analysis and optimization of pulse detonation engine parameters experimentally. The combustion tube length, diameter, Schelkin spiral dimensions were optimized for maximum thrust obtained from the PDE. Flow control and fire control systems were developed and used for the purpose. The installation of PDE as a sustainer in a missile was also undertaken and found that it can be integrated.
| Manpower Sanctioned/Hired | Manpower Trained |
|---|---|
|
RA (Nos): 01 |
Ph.D Produced: 2 |
|
Name of Equipment |
Make & Model |
Year of Purchase |
Cost |
Salient Features of Equipment |
Condition (Working /Not Working) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
National Instrument Data Acquisition system |
|
|
15.00 Lakh |
Data Acquisition @ 1 MHz |
Working |
|
PDE test Rig |
|
|
2.00 Lakh |
Test Rig |
Working |
| PI Details | Co-PI Details |
|---|---|
|
Dr. Sanjeev Kumar
Designation: Professor |
Dr. Arun Kumar Singh
Designation: Professor |
| Funding Agency | Project Cost |
|---|---|
| ER& IPR, DRDO, New Delhi. |
Rs. 30,28,450.00 |
| Start Date | Completion Date | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 2022-09-16 | Ongoing |
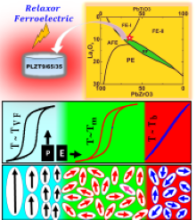
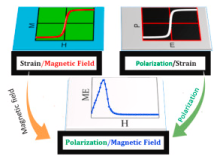
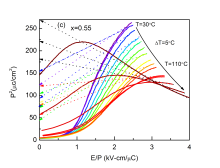
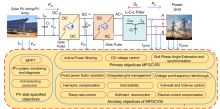
The aim of this proposal is to develop high Curie temperature lead free piezoceramics with superior piezoelectric properties. It is of our national importance to design, develop and scale up high Curie temperature lead free piezoceramics with superior piezoelectric properties. PI and his group will contribute to this through improvements, reliability and by improving the understanding of high Curie temperature lead free piezoceramics. Further impact derives from the training of early career researchers, employed in this project, who will provide the skills to transfer high Curie temperature lead free piezoceramics based technologies from academia to industry.
In this project, we will achieve the following goals:
- Curie temperature upto 450°C in chemically modified lead free BiFeO3-BaTiO3 solid solutions
- piezoelectric coefficient upto 200 pC/N in chemically modified lead free BiFeO3-BaTiO3 solid solutions
- A prototype piezoelectric vibration sensor (demonstration only) will be designed in consultation with domain scientist.
The project will also be benefitted from applicant’s existing links and joint research activities with Dr. O.P. Thakur, SSPL-DRDO, Prof. Rajeev Ranjan, Materials Engineering, IISc Bangalore, Prof. Ashish Garg, Materials Science and Engineering, IIT Kanpur and Dr. A.R. James, DMRL-DRDO.
| Manpower Sanctioned/Hired | Manpower Trained |
|---|---|
|
JRF (Nos): 01 |
|
Name of Equipment |
Make & Model |
Year of Purchase |
Cost (Rs.) |
Salient Features of Equipment |
Condition (Working /Not Working) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Microwave sintering furnce |
- |
- |
9,00,000/- |
This equipment will provide mircowaves for sintering of lead free relaxor ceramics. It will quite less time as compared to conventional sintering. |
- |
| PI Details | Co-PI Details |
|---|---|
|
Dr. Sanjeev Kumar
Designation: Professor |
Dr. Arun Kumar Singh
Designation: Professor |
| Funding Agency | Project Cost |
|---|---|
| Central Power Research Institute (CPRI), Bangalore |
Rs. 37,95,000.00 Amount Received till date (in Rs.) Rs. 27,85,900.00 |
| Start Date | Completion Date | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 2023-03-28 | Ongoing |
The aim of this proposal is to develop lead free relaxor ferroelectric materials with enhanced power density, very short discharge time, high breakdown strength for possible pulsed capacitor applications.
Materials with high power density and energy density are becoming gradually significant due to swift growth of advanced pulsed power systems for applications such as hybrid electric vehicles, high frequency inverters, space vehicle power systems, medical devices, electromagnetic rail guns etc, Energy storage devices mainly comprise of Fuel cells, lithium ion batteries, electrochemical capacitors and electrostatic capacitors. Batteries possess enormously high energy density but their output power is limited by the low mobility of charge carriers, which further restricts their application in pulsed power systems. Due to fast polarization response under an applied external electric field, dielectric materials exhibit very high charge/discharge speed which further results in a huge output power density of the order of MW.
From the last decade, relaxor ferroelectrics possess negligible Pr (remnant polarization), low coercive field and high Pmax (maximum polarization) due to their characteristic polar nano regions (PNRs), which further results in high energy density and efficiency. Therefore, the relaxor ferroelectrics are appreciated candidates in the field of energy storage applications. It is experimentally evidenced that DBS of bulk ceramic is associated with the microstructure, such as grain size, grain boundary condition, porosity etc. Among these, grain size contribution is quite prominent. Tunkasiri calculated the effect of grain size on DBS of the ceramic; E_DBS∝1/√G where, EDBS is the DBS of the ceramic and G is the grain size of the ceramic. To achieve our goal, the proposed research will concentrate on the following specific objectives:
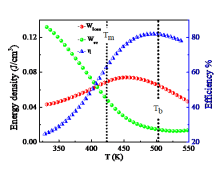
- To optimize the composition for the lead free (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3–BaTiO3 [NBT-BT] based solid solutions to achieve high value of breakdown strength > 200 kV/cm and recoverable energy density > 2 J/cm3.
- To study the effect of aging on power density and energy storage efficiency.
- To design and develop a pulse power capacitor with capacity ~1000 pF, operating temperature range -30 to +100°C, Vmax (DC) ~30kV.
| Manpower Sanctioned/Hired | Manpower Trained |
|---|---|
|
JRF (Nos): 01 |
|
|
Name of Equipment |
Make & Model |
Year of Purchase |
Cost (Rs.) |
Salient Features of Equipment |
Condition (Working /Not Working) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Pulse switching
|
- |
- |
12,00,000/- |
It will be used for fast charging and discharging of lead free ferroelectric materials. |
- |
|
High speed data acquisition system |
|
|
4,00,000/- |
It will record the high speed data during charging and discharging of lead free ferroelectric materials. |
|
|
Upgradation of poling unit |
|
|
2,00,000/- |
It will electrically pole the lead free ferroelectric materials. |
|
| PI Details | Co-PI Details |
|---|---|
|
Dr. Sanjeev Kumar
Designation: Professor |
| Funding Agency | Project Cost |
|---|---|
| ER& IPR, DRDO, New Delhi. |
Rs. 10,00,000.00 Amount spent till date (in Rs.) Rs. 9,92,552 |
| Start Date | Completion Date | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 2016-06-01 | 2018-03-31 | Completed |
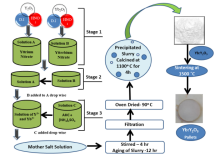
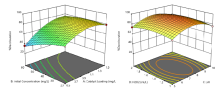
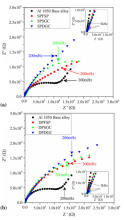
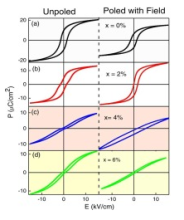
We have synthesized the PZT and Nb doped PZT samples using solid state reaction method. XRD studies clearly depict that there is no impurity phase present in the samples. Dielectric measurements show that the dielectric constant was below 500 as required for ferroelectric generator (FEG) applications. Ferroelectric measurements show that the remnant polarization for all samples is above 25 µC/cm2. We have also achieved high density to samples to become good candidate for FEG applications.
| Manpower Sanctioned/Hired | Manpower Trained |
|---|---|
|
JRF (Nos): 01 |
Ph.D Produced: 01 |
|
Name of Equipment |
Make & Model |
Year of Purchase |
Cost (Rs.) |
Salient Features of Equipment |
Condition (Working /Not Working) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1. High Temp. Furnace – 01 No. |
Jupiter Engg. works, New Delhi |
2017 |
2,65,000/- |
Robust furnace used for heating samples at 1550°C |
Working |
|
2. Ball Mill Machine – 01 No. |
Jupiter Engg. works, New Delhi |
2017 |
1,75,000/- |
For proper mixing of oxide powders |
Not Working |