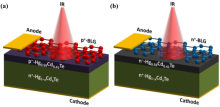
Bilayer Graphene/HgCdTe Heterojunction Based Novel GBn Infrared Detectors
| Abstract | We have demonstrated the different configurations of bilayer graphene (BLG)/mercury cadmium telluride (Hg1–xCdxTe) based GBn detectors operating in the mid- and long-wave infrared (IR) regime. The Silvaco Atlas TCAD software is used for the optoelectronic characterizations which closely matches the results obtained through analytical modeling. The proposed GBn detectors demonstrate about 106 times improvement in photocurrent density and self-powered mode operation. The proposed detectors demonstrate rapid photoswitching time <0.1 ps. The external quantum efficiency (QEext) of 26.06, 11.68, 54.08, and 50.53% are found for GpBpn mid-wave, GpBpn long-wave, GnBnn mid-wave, and GnBnn long-wave IR detectors, respectively, at –0.5 V and 77 K. Such detection performances are ascribed to the huge built-in electric field at contact/barrier heterojunction, and large barrier height in conduction band resulting in enhanced photogenerated carriers which contributes to the net photocurrent. Further, it is shown that the multiplication effect of carriers in BLG and high electric field across the interface results in the QEext >100% at near room temperature. |
| Faculty |
Arun Kumar Singh
Neena Gupta
Sanjeev Kumar
|
|
arun@pec.edu.in
|
|
| Collaborations | Dr Avishek Das, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Recife-PE, Brazil; Dr. Neha Sardana IIT Ropar |
| More Information | DOI: 10.1016/j.micrna.2022.207345; DOI 10.1088/1361-6528/ab9da8; DOI: 10.1109/TNANO.2019.2931814; DOI: 10.1039/C8RA07683A |