Characterization and Quasi-Static Compressive Response Of Closed Cell Al2024-B4Cp Composite Foams and Their Energy Absorption Characteristics
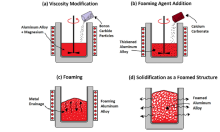
| Abstract | The applications of aluminum foams in the automobile and aerospace sector are growing day by day because of their unique properties such as high specific strength, greater stiffness, and higher energy absorption capacity. In the current work, the Al2024-B4Cp composite foams were developed by the direct foaming method. The effect of different sized B4C particles (fine particles: Average Particle size (APS) 5lm and coarse particles: APS 45lm) and its wt % (2, 4, 6, and 8) on foam characteristics, hardness, quasi-static compressive response, and energy absorption capacity was investigated. Varying B4C particle size and wt % had a significant impact on foam parameters such as foam expansion, relative density, cell size, and cell wall thickness. Hardness increases with increasing wt % of particles and fine particles added foam showed higher hardness than that of coarse particles added foam. An increase in wt % of particles improves the peak stress, plateau stress, and energy absorption capacity. Coarse particles added foam showed superior compressive properties and energy absorption capacity than that of fine particles added foam. |
| Faculty |
Dr. Jagmohan Datt Sharma
|
|
jdsharma@pec.edu.in
|
|
| Collaborations | Goswami Ganesh Dutta Sanatan Dharam College, Kheri Gurna, Patiala, Punjab 140417, India |
| More Information | DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-022-00837-2 |